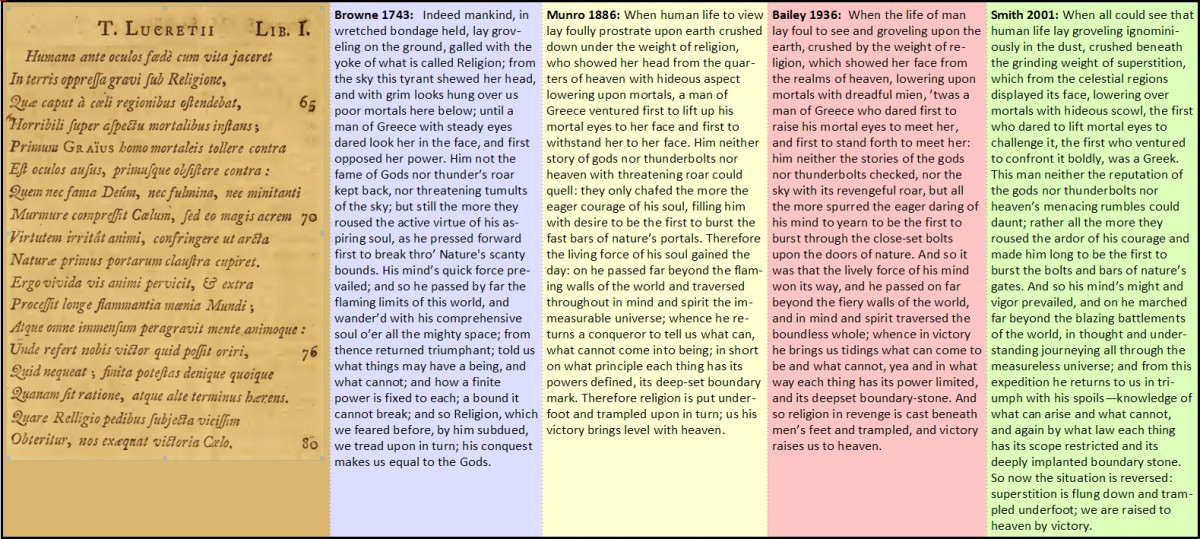
I think these side-by-side Latin and alternate translations are helpful. Slight word changes can lead to significant changes in meaning, and translators tend to add or subtract words depending on their own view of what a passage "should" mean. Here is perhaps the most famous passage of all from Lucretius Book 1 -
Munro: "When human life to view lay foully prostrate upon earth crushed down under the weight of religion, who showed her head from the quarters of heaven with hideous aspect lowering upon mortals, a man of Greece ventured first to lift up his mortal eyes to her face and first to withstand her to her face. Him neither story of gods nor thunderbolts nor heaven with threatening roar could quell: they only chafed the more the eager courage of his soul, filling him with desire to be the first to burst the fast bars of nature’s portals. Therefore the living force of his soul gained the day: on he passed far beyond the flaming walls of the world and traversed throughout in mind and spirit the immeasurable universe; whence he returns a conqueror to tell us what can, what cannot come into being; in short on what principle each thing has its powers defined, its deep-set boundary mark. Therefore religion is put underfoot and trampled upon in turn; us his victory brings level with heaven."